|
|
| Malfunction Code Descriptions |
For Buick 3.8L V6 SFI Turbo CCCI 84-87 Models
|
|
What do you do when this famous light turns on?
| SERVICE ENGINE SOON |
The first thing you need to do is find out what malfunction code(s) are presently set in the ECM. You can read these malfunction codes in several different ways. The best and easiest way is to purchase a "SCAN" tool like Diacom or Turbolink and they will conveniently read and store the code for you. The other method is to perform a "NON-SCAN" diagnostic circuit check which causes the "Service Engine Soon" light to blink the codes set in the ECM.
The following "NON-SCAN" method can be used to read these codes.
A steady "Service Engine Soon" light with ignition "ON" and engine stopped confirms battery and ignition voltage to the Electronic Control Module (ECM).
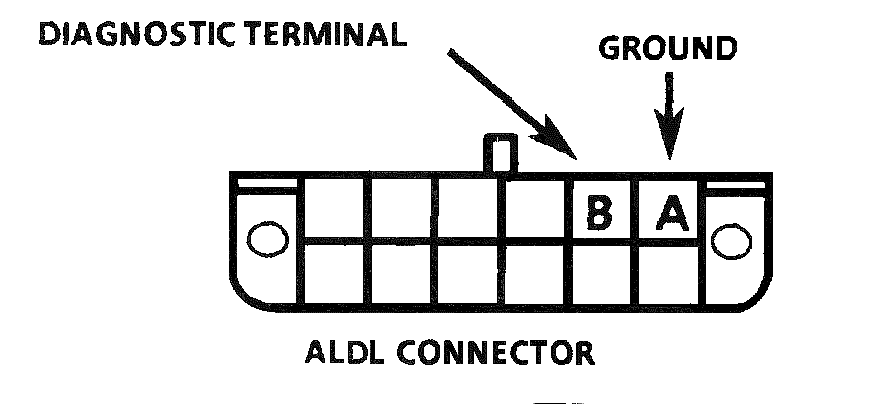
1. First you must locate the ALDL connector which is located below the instrument panel (under radio).
The ALDL connector looks like this 
2. With ignition "ON" and engine "NOT RUNNING" use a jumper (paper clip) and connect terminal "B" to terminal "A". Terminal "A" is the ground connection.
3. The ECM will cause the "Service Engine Soon" light to flash Code 12, indicating that the ECM diagnostics are working. Code 12 will flash three (3) times, followed by any other trouble codes stored in memory. Each additional code will flash three (3) times, starting with the lowest code, and then start over again with Code 12. If there are no other codes, Code 12 will flash until the diagnostic jumper is disconnected or the engine is started.
Example: An error Code 13 will be: 12,12,12,13,13,13,12,12,12, any more Codes...
4. To clear the codes, shut the ignition "OFF" and remove the ECM supply voltage for 10 seconds. This is the orange wire and connector located behind the battery. Re-connecting this wire will cause the ECM to reset which clears the Malfunction Codes.
If the codes are not cleared manually, they will be cleared by the ECM after 50 engine starts with no malfunctions.
The following chart gives Code # and Description of Malfunction.
The Malfunction Code descriptions and troubleshooting steps were reproduced (with permission) from the TurboLink (by TDS Technologies) malfunction screens. The conditions for each error were determined by analysis of the actual 1986 / 87 turbo Regal ECM code.
Click on Error Code number or Malfunction Description to get detailed information.
Trouble Code 12 is a special case code that is not logged into the ECM's Non-Volatile Memory (NVM) when detected. When the ignition is "ON" and the ECM detects no ignition reference pulses coming from the ignition module, it illuminates the Service Engine Soon lamp.
Code 12 is also used when the ECM is in Diagnostic mode (ALDL Terminal B grounded, key On, engine Off) to signal the beginning or end of a so-called 'diagnostic sequence'. This is when the ECM enunciates each stored code using the instrument panel Service Engine Soon lamp.
When in this mode, the ECM will begin by flashing code 12 (on the lamp) 3 times. This indicates the beginning of a diagnostic sequence. It will then flash any codes stored in NVM 3 times each before proceeding to the next code. When all stored codes have been displayed, the ECM will again flash code 12 to indicate the end of the diagnostic sequence. The cycle continues as long as the ECM is in Diagnostic Mode.
NOTE: The codes will not be displayed in order of occurrence but rather in numerical order.
Trouble Code 13 indicates that the exhaust stream oxygen content sensor (O2 sensor) is not responding as expected. When cold, the sensor is 'biased' by the ECM to about 450 millivolts. Before it warms to at least 600 deg F (315 deg C) it acts as an open circuit and when the ECM reads it, it reads the 450 mV bias. The ECM expects the sensor to warm in a short period of time and begin sending its own voltages.
The conditions for setting this code are:
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Defective or degraded O2 sensor
2) Deposit contaminated O2 sensor (running leaded fuel, RTV silicone deposits etc.)
3) Corroded/defective O2 sensor connection
4) Defective sensor ground circuit
5) Defective connection at ECM
6) Defective ECM
Trouble Code 14 indicates that the Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS) is reporting abnormally high readings. CTS is used to control fuel mixture, timing, idle speed, TCC and EGR operations among others. The thermistor used has a low resistance when hot, rising as the coolant cools. This error then, indicates a very low resistance in the CTS circuit.
The conditions for setting this code are:
NOTE: A default temperature of 111 deg F is used while the error is present.
Typical thermistor resistance values are:
| deg F | deg C | resistance (ohms) |
|---|---|---|
| 210 | 100 | 185 |
| 160 | 70 | 450 |
| 100 | 38 | 1,800 |
| 70 | 20 | 3,400 |
| 40 | 4 | 7,500 |
| 20 | -7 | 13,500 |
| 0 | -18 | 25,000 |
| -40 | -40 | 100,000+ |
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Severe engine overheating
2) Defective Coolant Temperature Sensor (resistance too low)
3) Short circuit in CTS-ECM harness
4) Defective ECM
Trouble Code 15 indicates that the Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS) is reporting abnormally low readings. CTS is used to control fuel mixture, timing, idle speed, TCC and EGR operation, among others. The thermistor used has a high resistance when cold, lowering as the coolant warms. This error then, indicates a very high resistance in the CTS circuit.
The conditions for setting this code are:
NOTE: A default temperature of 111 deg F is used while the error is present.
Refer to the Code 14 description for typical sensor resistance values.
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Open circuit in CTS-ECM harness
2) Defective Coolant Temperature Sensor (resistance too high)
3) Open sensor ground circuit
4) Defective ECM
Trouble Code 21 indicates that the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is reading abnormally high. TPS volts should be close to 0.42 V at closed throttle and rise smoothly in about 0.02 volt increments to a maximum reading of about 4.85 volts at WOT.
The conditions for setting this code are:
- or -
Note: During a Code 21 condition, the ECM uses a default TPS value of 2.6 volts. This will cause the engine to idle very high.
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Defective TPS
2) Short circuit in the TPS harness to +5 volt reference
3) Open sensor ground circuit
4) Defective ECM
Trouble Code 22 indicates that the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is reading abnormally low. TPS volts should be close to 0.42 V at closed throttle and rise smoothly in about 0.02 volt increments to a maximum reading of about 4.85 volts at WOT.
The conditions for setting this code are:
Note: During a Code 22 condition, the ECM uses a default TPS value of 2.6 volts. This will cause the engine to idle very high.
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Maladjusted TPS
2) Defective TPS
3) No +5 volt reference to TPS
4) TPS-return to ECM is shorted to ground or to sensor ground
5) Defective ECM
NOTE: The TPS must be adjusted to about 0.42 volts at closed throttle for the ECM to auto-zero properly. If necessary, adjust the TPS to bring the voltage up or down to this value at closed throttle.
Trouble Code 23 indicates that the Manifold Air Temperature (MAT) sensor is reporting abnormally low readings. When the air is cold, the thermistor in the sensor has a high resistance, which falls as the air charge warms. Low readings thus indicate a possible bad sensor or open in the MAT circuit.
The conditions for setting this code are:
NOTE: A default MAT value indicating 82 deg F is used while Code 23 is present.
Typical thermistor resistance values are:
| deg F | deg C | resistance (ohms) |
|---|---|---|
| 210 | 100 | 185 |
| 160 | 70 | 450 |
| 100 | 38 | 1,800 |
| 70 | 20 | 3,400 |
| 40 | 4 | 7,500 |
| 20 | -7 | 13,500 |
| 0 | -18 | 25,000 |
| -40 | -40 | 100,000+ |
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Defective MAT sensor
2) Open sensor ground circuit
3) Dirty or corroded connection(s) at MAT and/or ECM
4) Open circuit between the ECM and the MAT sensor
5) Defective ECM
Trouble Code 24 indicates that the Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) is reporting an abnormally low reading when other sensors indicate it should be higher.
The conditions for setting this code are:
If the code was logged when the vehicle was in motion, the following should be checked:
1) Defective or corroded VSS connections
2) Maladjusted TPS sensor. The TPS should read about 0.42 volts at closed throttle
3) Defective speedometer cable
4) Bad or missing speedo drive gear(s) in tail shaft housing of the transmission
5) Defective VSS
6) Defective ECM
Trouble Code 25 indicates that the Manifold Air Temperature (MAT) sensor is reporting abnormally high readings. When the air is hot, the thermistor has a low resistance, which rises as the air temperature cools. High readings thus indicate a possible bad sensor or short in the MAT circuit.
The conditions for setting this code are:
Refer to the Code 23 description for typical sensor resistance values.
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Defective MAT sensor
2) MAT signal shorted to ground or to sensor ground
3) Defective ECM
Trouble Code 31 indicates that the Wastegate Solenoid may not be functioning correctly. The wastegate solenoid is controlled by a Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) signal from the ECM. The ECM controls turbo boost by varying the PWM waveform (duty cycle) to the wastegate. The wastegate responds by bleeding off exhaust pressure upstream of the turbine, thus controlling boost pressure.
The conditions for setting this code are:
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Poor or corroded connections between the ECM and the wastegate solenoid
2) Open or shorted solenoid
3) Defective, sticking or maladjusted wastegate linkage
4) Defective ECM
Ensure correct operation of other engine subsystems, including but not limited to the TPS and MAF sensors and check the wastegate actuation hardware.
Trouble Code 32 indicates that the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve diaphragm is not where the ECM expects it to be. The ECM controls the diaphragm with a Pulse-Width Modulated (PWM) waveform. The EGR has a vacuum bleed solenoid that adjusts the vacuum applied to the EGR valve based on this pulse width. If there is sufficient vacuum at the EGR valve, a switch closes to send a signal back to the ECM. The absence of this signal is the bases for code 32.
The conditions for setting this code are:
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Faulty EGR valve-to-ECM connection
2) Plugged EGR passages and/or sticking EGR valve
3) Defective EGR valve
4) Defective ECM
Trouble Code 33 indicates that the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor is reporting more air is entering the engine than makes sense based on RPM and TPS. The MAF sensor produces a frequency output; around 30 Hz at idle to 150 Hz under acceleration. The frequency varies proportionally to airflow. The ECM monitors the frequency and thus determines airflow into the engine. Typical idle MAF is 5 to 7 grams per second.
The conditions for setting this code are:
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Faulty MAF-to-ECM connection
2) Exceedingly noisy spark plug wires
3) Poor routing of MAF harness (i.e. near coil packs)
4) Maladjusted TPS sensor
5) Defective MAF sensor
6) Defective ECM
Trouble Code 34 indicates that the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor is reporting less air is entering the engine than makes sense based on RPM and TPS. The MAF sensor produces a frequency output; around 30 Hz at idle to 150 Hz under acceleration. The frequency varies proportionally to airflow. The ECM monitors the frequency and thus determines airflow into the engine. Typical idle MAF is 5 to 7 grams per second.
The conditions for setting this code are:
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Faulty air ducting to or from MAF sensor
2) Faulty ECM-to-MAF connections
3) Poor routing of MAF harness (i.e. near coil packs)
4) Maladjusted TPS sensor
5) Defective MAF sensor
6) Defective ECM
Trouble Code 35 is not used in the Turbo cars. If this code appears while a computer is connected to the ALDL connector, it is probably the result of a bad cable connection at the PC or the ALDL connector. Reseat the cable connections.
Trouble Code 41 indicates that the Camshaft Sensor is not functioning properly.
The ignition module uses the Cam Sensor signal for timing the spark firing. The ignition module also passes this signal to the ECM to enable sequential fuel injection. The inability to properly determine engine position from the Cam Sensor will generate Code 41.
The engine will continue to run if the signal is lost from the sensor, however it will not restart after shut down. If the Cam signal from the ignition module to the ECM is lost while running, the ECM will switch to the simultaneous fuel injection mode. The engine can be re-started but will continue to run in the simultaneous mode as long as the fault is present.
The conditions for setting this code are:
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Loose or misadjusted Cam Sensor
2) Defective Cam Sensor-to-ECM connections
3) Defective ECM
Cam sensor installation and adjustment procedures call for very exact tolerances. It is for this reason that it is recommended that the service manual be consulted while performing any adjustment or replacement of the Camshaft Sensor.
Trouble Code 42 indicates that there may be a malfunction in the Electronic Spark Timing (EST) system.
During cranking, the timing is controlled by the ignition module while the ECM monitors the engine speed. When the engine speed exceeds 400 RPM, the ECM sends a BYPASS signal to the ignition module which switches the timing to ECM control. The ECM calculates what the timing should be then "tells" the ignition module via the EST circuit.
An open or ground in the EST circuit will stall the engine and set a Code 42. The engine can be re-started but it will run on ignition module timing.
The conditions for setting this code are:
- or -
Typical causes for this code include:
1) BYPASS line is open or grounded
2) EST line is open or grounded
3) PROM or CALPACK not seated properly in the ECM
4) Poor connections between ignition module and ECM
5) Poor routing of EST harness and/or poor quality ignition wires (EMI induced electrical noise)
6) Faulty or incorrect ignition module
7) Faulty ECM
Trouble Code 43 indicates that there may be a malfunction in the Electronic Spark Control (ESC) circuit.
ESC is used to sense spark knock (pinging) and retard the timing to eliminate it. A knock sensor (located at the rear of the engine block) sends signals to an ESC module which then signals the ECM that knocking is being detected. The ECM will retard the timing by as much as 20 degrees in 1 degree increments. A loss of knock sensor signal or loss of ground at the ESC module will cause the signal at the ECM to remain high. The ECM will act as if no knock is present, and may possibly result in engine damage, if there is detonation.
Loss of the ESC signal to the ECM will cause the ECM to constantly retard the timing to its maximum. This results in sluggish performance and a Code 43.
The conditions for setting this code are:
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Open or shorted knock sensor
2) Loose knock sensor
3) Excessive mechanical noise within engine
4) Improper or incorrectly installed PROM or CALPACK in the ECM or defective ECM
5) Intermittent open in the EST line to the ignition module
Trouble Code 44 indicates that the O2 sensor is showing a persistently high exhaust oxygen content (lean), despite the efforts of the ECM to increase injector on-time (thus increasing fuel delivered). Integrator and BLM numbers may indicate > 128 by a substantial margin.
The conditions for setting this code are:
Typical causes for this code include:
1) O2 sensor defective or lead shorted
2) Lean injectors (dirty or blocked)
3) Water in fuel
4) Exhaust leaks upstream of O2 sensor
5) Fuel pressure or volume too low
6) MAF sensor reading lower airflow than is actually present
7) Vacuum leaks
8) Incorrect or poorly calibrated PROM
Trouble Code 45 indicates that the O2 sensor is showing a persistently low exhaust oxygen content (rich), despite the efforts of the ECM to decrease injector on-time (thus decreasing fuel delivered). Integrator and BLM numbers may indicate < 128 by a substantial margin.
The conditions for setting this code are:
Typical causes for this code include:
1) O2 sensor defective or contaminated (if incorrect RTV sealant or too much RTV is used, this may happen)
2) Leaking fuel injectors
3) Fuel pressure too high
4) EMI interference from poor plug wires
5) Evaporative Emission system defect
6) TPS and/or EGR problem
7) MAF sensor reading higher airflow than is actually present
Trouble Code 51 indicates that the ECM sensed a fault in the PROM.
When the PROM was initially created, a checksum number representing the total of all the cell values was also stored. The ECM uses this checksum as one way to determine if the contents of any cell has changed. A Code 51 causes the ECM to enter Back-Up mode which uses the CALPAK for default sensor values.
The conditions for setting this code are:
- or -
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Incorrectly installed PROM module
2) Defective PROM module
3) Defective ECM
Trouble Code 52 indicates that the ECM sensed a fault with the CALPACK. The CALPACK is a plug-in module separate from the PROM, that contains preset calibrations used by the system during "limp home" (backup) mode. The ECM continuously checks for its presence while power is applied.
The conditions for setting this code are:
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Incorrectly installed CALPACK module
2) Incorrect CALPACK module for this vehicle
3) Defective or incorrectly inserted PROM
4) Defective ECM
Trouble Code 53 refers to a feature never actually installed on any turbo Regal. This code was reserved when these vehicles where being developed, in the event that water injection hardware would be installed in production vehicles.
Since water injection was never actually used, this code should never appear.
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Incorrect PROM installed in the ECM
2) PROM incorrectly installed in the ECM
3) Defective PROM
Some after market PROMs, particularly those designed as 'off road use only', may not properly deal with trouble codes. If it is suspected this is causing a Code 53, contact the PROM manufacturer.
Trouble Code 54 is not used by the turbo cars. If this code does appear, it is probably due to a loose connection or bad ground. If a computer is connected to the car's ALDL connector when the code appears, check the computer cable connections.
Trouble Code 55 indicates that the Analog-to-Digital (A/D) converter in the ECM is faulty. This converter reads sensors (e.g., TPS, Oxygen) and coverts their analog voltage output to a digital number for use by the ECM. If the converter fails, the ECM sets this code.
The conditions for setting this code are:
Typical causes for this code include:
1) Defective or incorrectly inserted PROM
2) Defective ECM
If replacing the ECM, be sure to transfer both the PROM and the CALPACK from the old unit. If the old ECM also indicated PROM failure (Code 51) or a bad CALPACK (Code 52), be sure to verify these components are fully operational in the new unit. If they are not, they too will have to be replaced.
Last updated: